Dominica is a mountainous Caribbean island nation distinguished by geothermal hot springs.
The official name of the country is the Commonwealth of Dominica.
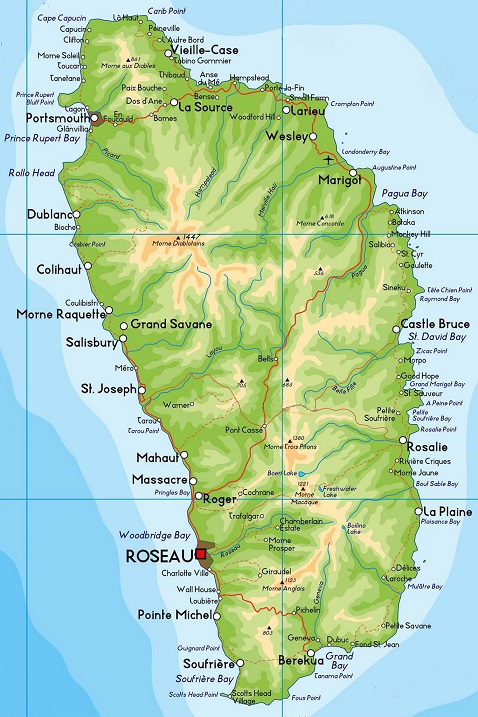
Dominica is part of the Windward islands in the Lesser Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean Sea.
The island faces the Atlantic Ocean to the east and the Caribbean Sea to the west. Its nearest neighbors are the French islands of Guadeloupe to the north and Martinique to the south.
As of 1 January 2016, the population of Dominica was estimated to be 72,665 people.
The official language is English.
The island has an area of 754 square kilometers (291 square miles) and is 47 kilometers (29 miles) long by 26 kilometers (16 miles) wide, with a coastline of 148 kilometers (92 miles).
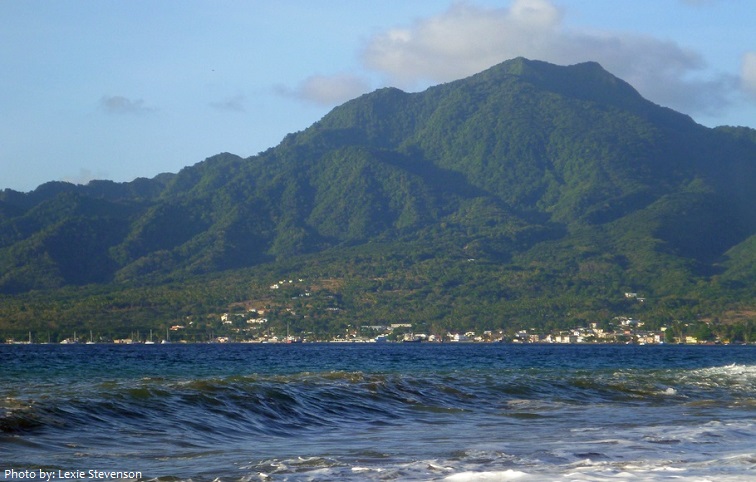
The whole land mass is of recent volcanic formation, and the mountain peaks are cones of volcanoes with lava craters and small lakes of boiling water.
Roseau is the capital and largest city of Dominica, with a population of about 16,500. It is a small and compact urban settlement surrounded by the Caribbean Sea, the Roseau River and Morne Bruce.
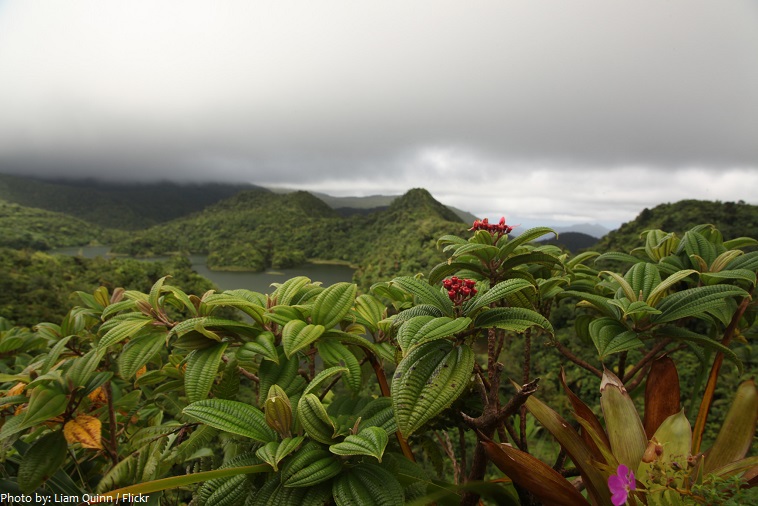
The majority of the island is covered by densely wooded mountains and rainforest. The overall terrain is very steep, and extremely rugged.
The highest mountain peak on Dominica, at 1,447 meters (4,747 feet), is Morne Diablotins, which is also the second highest mountain in the Lesser Antilles.
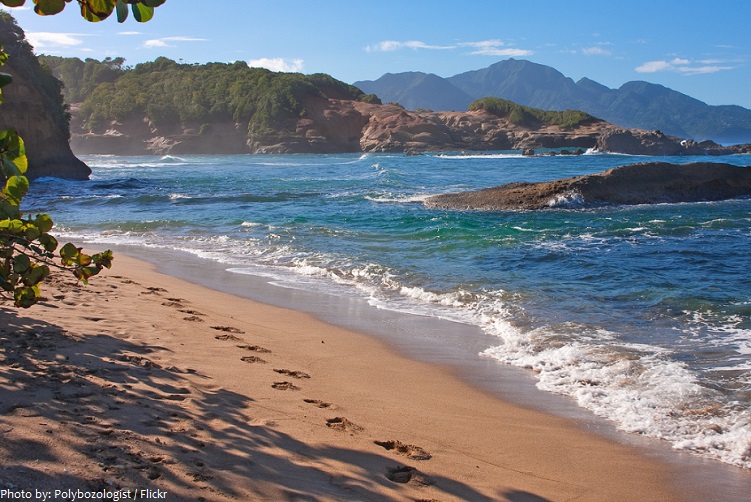
A thin coastal strip lies between the sea and the mountains. The seas are crystalline, the coast is rugged and the cliffs are dramatic. The sand is not typical of islands in the region. Visitors to Dominica will not find white, pristine beaches, but rather black and yellow volcanic sand.
Dominica is often known as “The Nature Island of the Caribbean” due to its spectacular, lush, and varied flora and fauna, which are protected by an extensive natural park system.
There are three national parks in Dominica. Other protected areas include two forest reserves and the Syndicate Parrot Preserve.
Morne Trois Pitons National Park is a UNESCO World Heritage Site since 1997. This national park stretches across nearly 7,000 hectares (17,000 acres) of Dominica’s mountainous volcanic interior. It’s a stunning pastiche of lakes, fumaroles, volcanoes, hot springs and dense tropical forest.
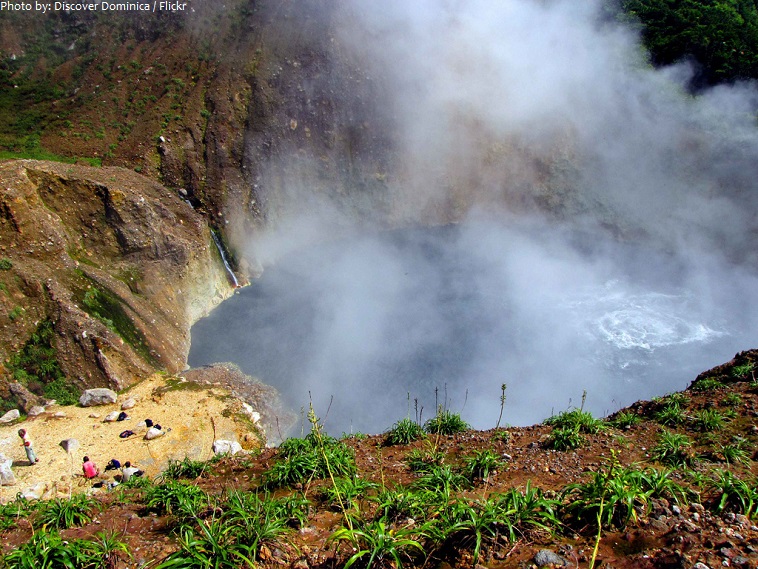
Dominica’s Boiling Lake is situated in the Morne Trois Pitons National Park. With approximately 60 meters (200 feet) to 75 meters (250 feet) across, it is the second largest hot spring in the world. The lake is filled with bubbling greyish-blue water that is usually enveloped in a cloud of vapour.
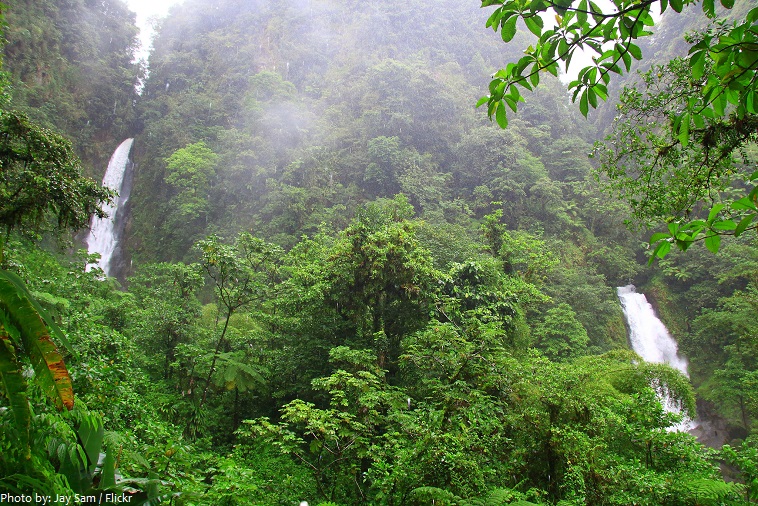
Dominica is blessed with 365 rivers, and lush oceanic rainforest hides dozens of waterfalls.
One of the most impressive and photogenic waterfalls on the island, the Victoria Waterfall, in Morne Trois Pitons National Park, is formed by the White River cascading over a cliff into a warm pool below. Minerals give the water a milky-white color.
Spectacular twin Trafalgar Falls are one of Dominica’s most famous sites. A combination of two waterfalls named the ‘mother’ (on the left) and ‘father’ (on the right), they have deep pools and a small hot water springs nearby.
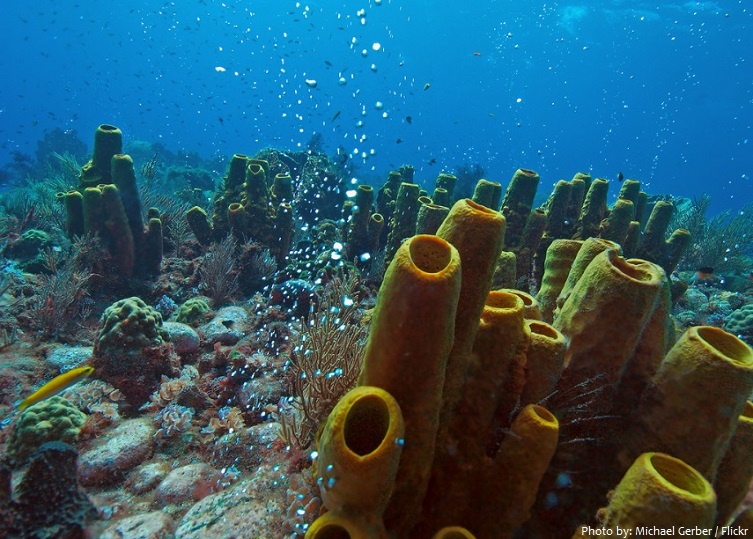
Dominica’s most famous dive and snorkel site, Champagne Reef lies in a marine reserve off the country’s southwest coast. Geothermal activity causes thousands of bubbles to emerge from beneath the rocks, a few meters from shore. Frogfish, flying gurnards, squid, and sea horses are just some of the species found in the warm waters here.
Before Europeans, the island was inhabited by the Kalinago people (Island Caribs).
Christopher Columbus spotted the island on Sunday 3 November 1493 and named it after the day of the week (dies Dominica in Latin, literally day of the Lord).
Dominica was claimed by Britain and France until 1763, when it was formally ceded to Britain.
On November 3rd, 1978 Dominica gained its independence from Great Britain and became an independent republic within the Commonwealth.
Most Dominicans are descendants of African slaves brought in by colonial planters.
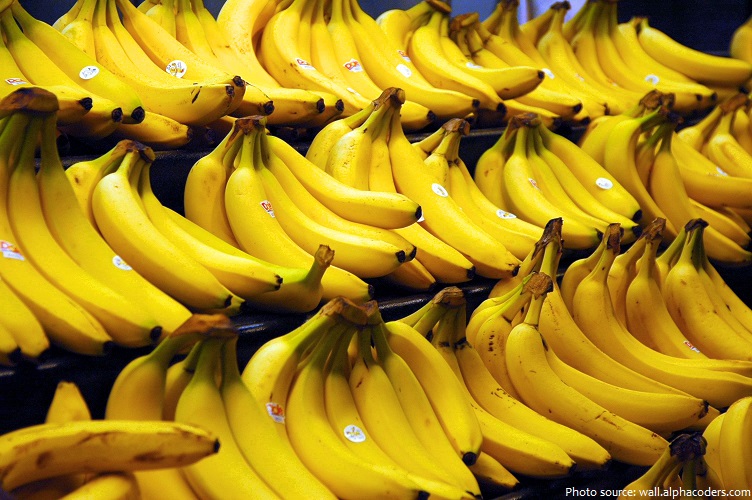
Bananas and other agriculture dominate Dominica’s economy, and nearly one-third of the labour force works in agriculture.
The Commonwealth of Dominica is becoming in recent years a major international financial center. The largest sectors are “offshore banking, payment processing companies, and general corporate activities”.
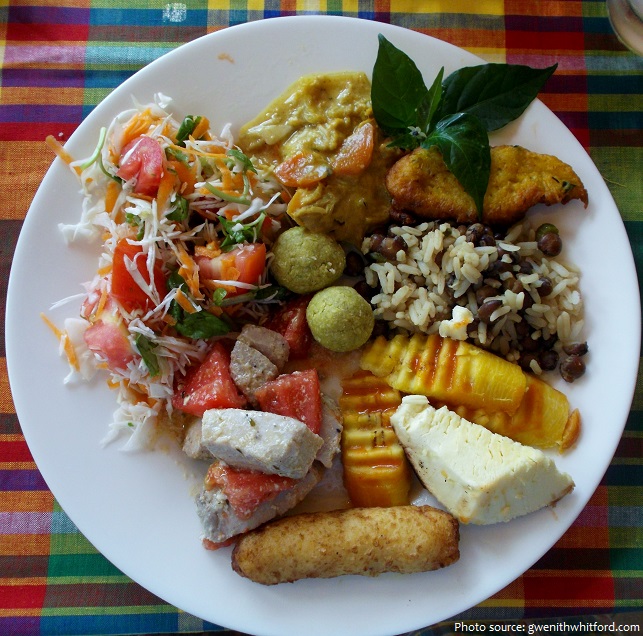
Dominica’s cuisine is similar to many other Caribbean islands. The cuisine is rooted in creole techniques with local produce flavored by spices found on the island.
Music and dance are important facets of Dominica’s culture. The annual independence celebrations display a variety of traditional song and dance. Since 1997, there have also been weeks of Creole festivals, such as “Creole in the Park” and the “World Creole Music Festival”.
Dominica has the largest remaining tribe of Carib Indians, also called Kalinago people, in the Caribbean.
Dominica’s original name is “Wai’tukubuli” which means “tall is her body” in the Kalinago language.
Dominica was the last island to be formed in the Caribbean.
There are 195 recorded species of fern, 75 kinds of orchids, 50 kinds of butterflies and 176 species of birds!
Much of the Walt Disney film Pirates of the Caribbean: Dead Man’s Chest, was shot on location on Dominica (though in the film it was known as “Pelegosto,” a fictional island), along with some shooting for the 3rd film in the series, At World’s End.