Bats are the only mammals capable of true flight.
Bats can be found almost anywhere in the world except the polar regions and extreme deserts.
There are about 1,200 different bat species.
They are divided into two main types: megabats and microbats.
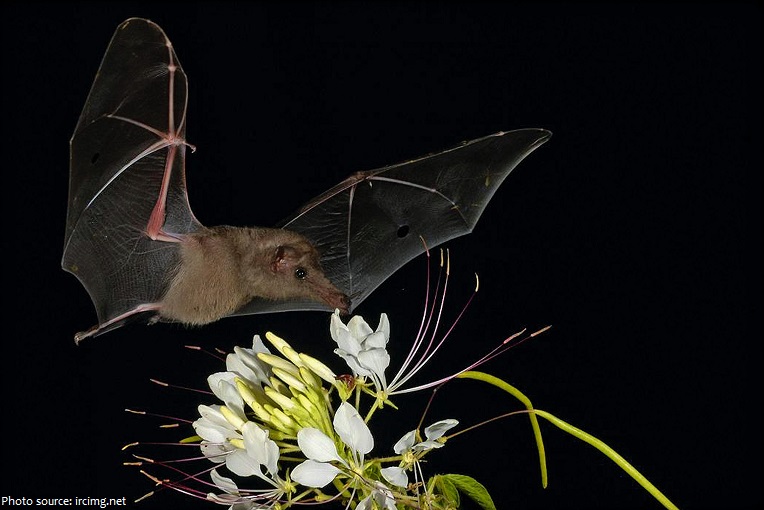
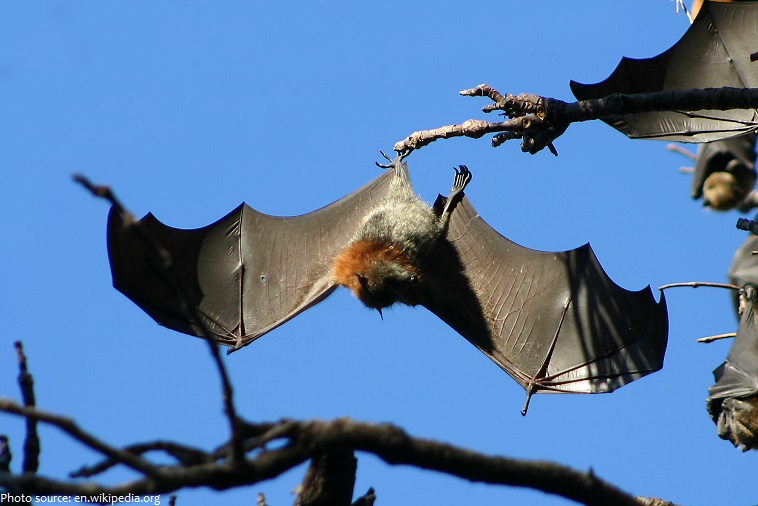
Megabats also called fruit bats, Old World fruit bats or flying foxes are medium to large-size bats. Many eat fruit, pollen, or nectar; some eat small land animals, and some eat fish.
Microbats are smaller bats that eat mostly insects. But not all megabats are larger than microbats.
The average lifespan of a bat is usually up to 20 years. Five species have been recorded living over 30 years in the wild.
The large flying fox (Pteropus vampyrus) is the largest species of bat. It weighs 0.65–1.1 kilograms (1.4–2.4 pounds) and has a wingspan of up to 1.8 meters (6 feet). Its head-body length is 27–32 centimeters (11–13 inches).
Kitti’s hog-nosed bat (Craseonycteris thonglongyai), also known as the bumblebee bat is the smallest species of bat and is considered the world’s smallest mammal. It grows to only about 3 centimeters long (1.25 inches) and weighs about 2 grams (0.07 ounces).
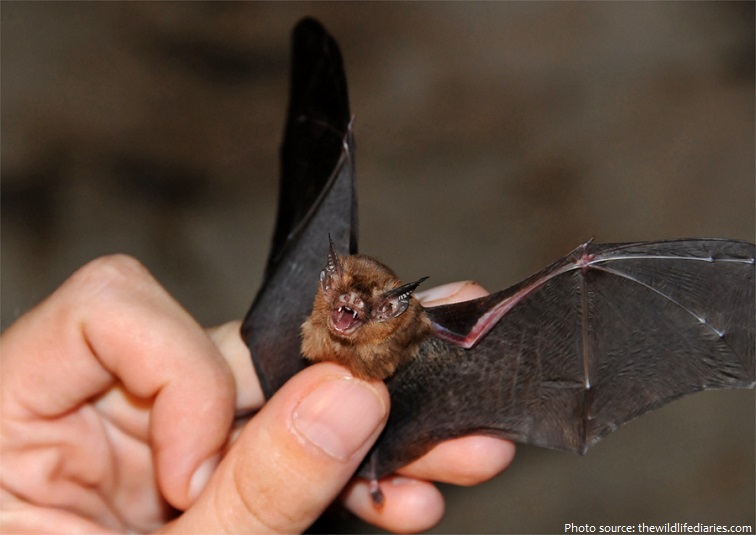
The mouth of a bat is similar to the one of a rat or fox. They have large, pointed ears and brown, gray or black fur.
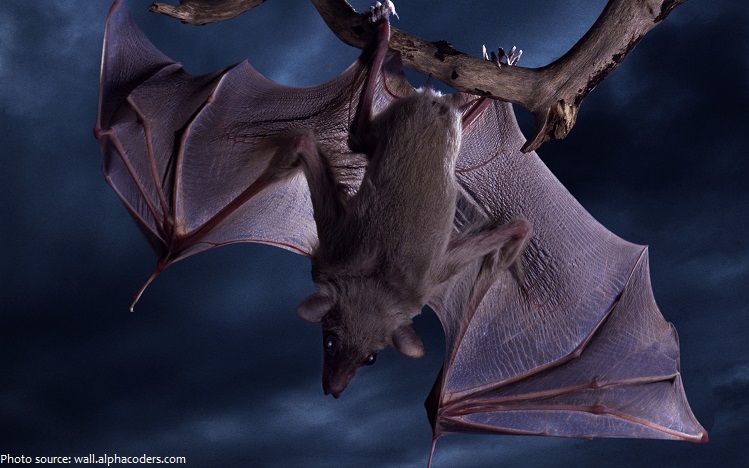
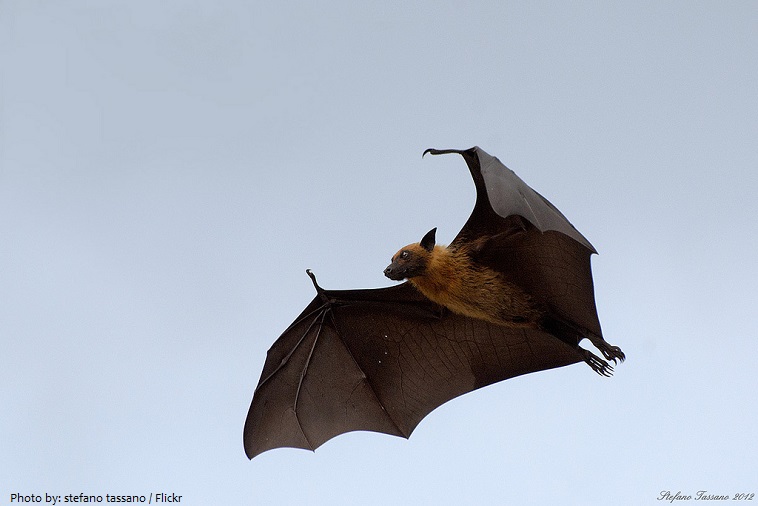
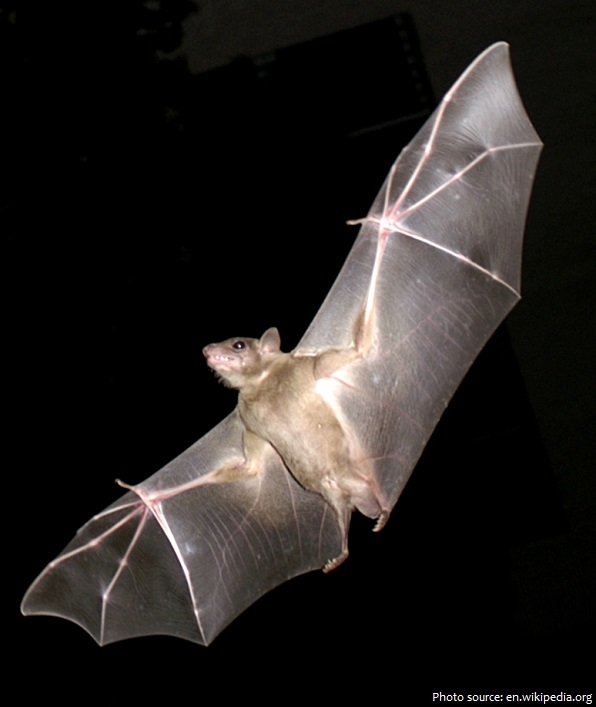
The wings of bats are their most distinctive – and perhaps most remarkable – feature. Bats have long arms and hands with especially long fingers. These are connected to the bat’s back and legs with a thin, strong membrane of soft, velvety skin, which form their wings.
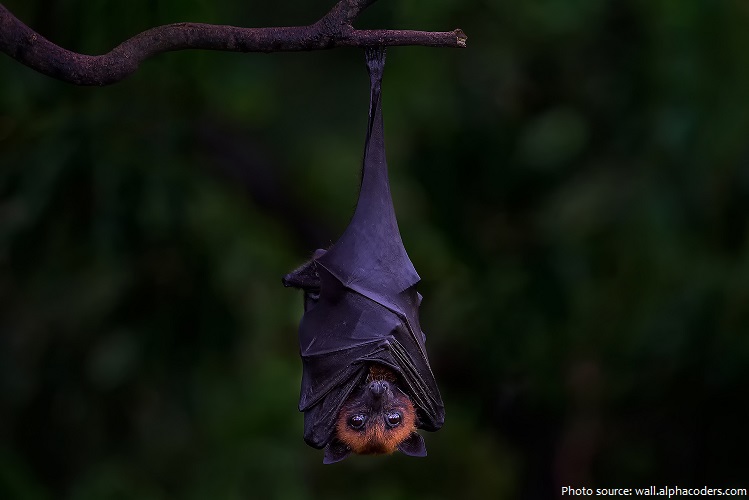
Bats roost upside down, since the lightweight bones in their hind legs cannot support their body weight in an upright position. Their wings wrap around them like a cloak while they rest.
They roost in trees, caves, mines and barns — anyplace that provides shelter from the weather, protection from predators and seclusion for rearing the animals’ young.
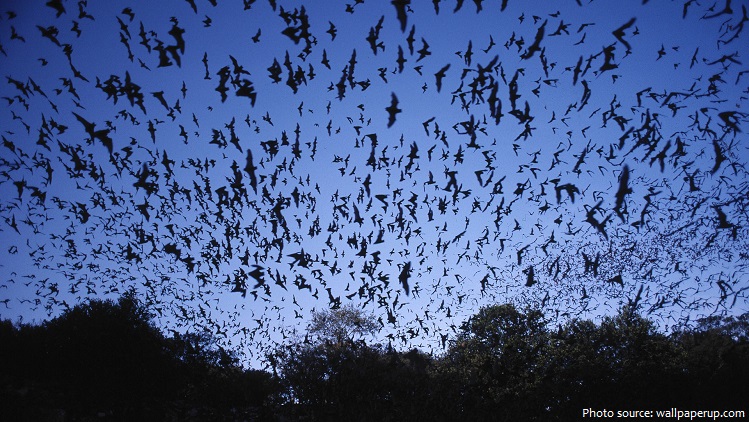
Some species are solitary while others form colonies of more than a million individuals. Largest known colony is found in the North America, where 20 million bats reside inside the Bracken Bat Cave in Texas.
Bats are nocturnal animals, meaning that they sleep during the day and are awake at night. They are most active during twilight. Some may fly up to 50 kilometers (31 miles) to find food during their nightly journeys.
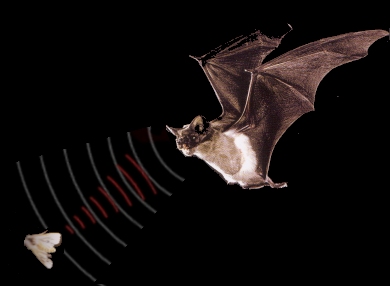
The microbats use echolocation to find their insect meals. They are able to “see” their world and detect prey by emitting short bursts of high-pitched sounds that bounce off objects and return to the bat as echoes.
As fruit doesn’t fly, megabats (fruit bats) lack complex echolocation. Instead, they rely on excellent eyesight and a good sense of smell to find their food.
Bats perform the vital ecological roles of pollinating flowers and dispersing fruit seeds; They are also economically important, as they consume insect pests, reducing the need for pesticides.
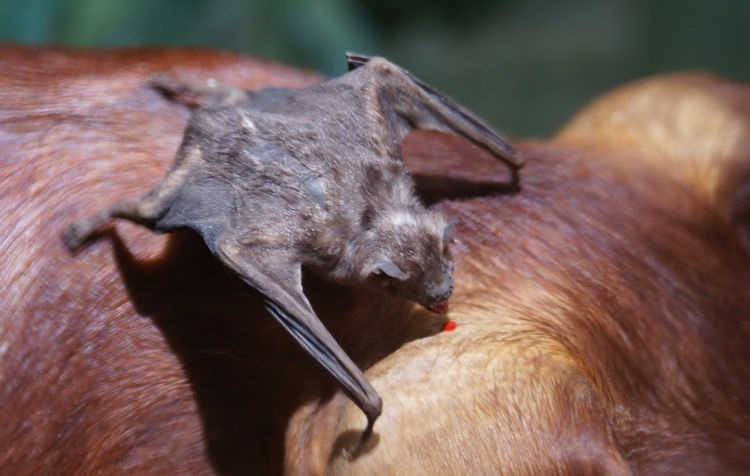
70% of all bats eat insects. Most of other bats consume fruits and nectar. A few species of bats eat fish, plus lizards, frogs, birds, rodents, and even other bats! And only three species dine on the blood of mammals.
Blood-eating species live in Mexico, Central America and South America. These bats make a small, V-shaped cut in the animal’s skin with a bite and then lick up the blood. A chemical in the bat’s saliva keeps the blood from clotting before the bat is done eating.
Some bats migrate to warmer climates during the winter, while others hibernate. One species travels 3,900 kilometers (2,400 miles) each year! It is not yet known how bats navigate these long distances to find the same cave they used the year before.
Most bats have a breeding season, which is in the spring for species living in a temperate climate. Male bats may sing, display their wings, or expand long hairs on the top of the head to attract a mate, depending on the species.
Most adult female bats have only one baby, called a pup, per year, although twins or quadruplets occur in a few species. All bats live on milk from birth up to six months of age. Female bats nurse their young until they are nearly adult size, because a young bat cannot forage on its own until its wings are fully developed.
Hawks and owls regularly kill and eat bats. Snakes and predatory mammals such as weasels and raccoons climb into bat roosts during the day and attack bats when they are sleeping. In some places, bats are even killed by little birds that fly into bat caves and peck them to death.
Bats are the second largest order of mammals (after the rodents), representing about 20% of all classified mammal species worldwide.
The term “blind as a bat” isn’t really accurate, since not one of the approximately 1,200 species of bat is inherently blind.
A mother bat can locate her pup by its scent and sound out of millions in a roost.
Vampire bats adopt orphaned young.
Most bats take off by dropping from a hanging position, and many can’t take off from the ground.
Mexican Long-tails are one of the fastest bats, and have been recorded flying at 96 kilometers (60 miles) per hour, at altitudes of over 3,000 meters (10,000 feet).
Bat finger bones are very flexible, with cartilage that lacks calcium and other minerals nearer the tips so they can bend without splintering.
Bat wings are laden with blood vessels, which help them heal rapidly if injured.
Bats belong to the taxonomic order Chiroptera, which means “hand wing.”
In European cultures, bats have long been associated with witchcraft, black magic and darkness.
In Mesoamerican mythology during the Classic-Contemporary period, bats symbolized the land of the dead, which was considered to be the underworld.
Among some Native Americans, such as the Creek, Cherokee and Apache, the bat is a trickster spirit.
Not all legends surrounding bats are negative, Chinese lore claims that the bat is a symbol of longevity and happiness, and is similarly lucky in Poland, geographical Macedonia and among the Kwakiutl and Arabs.
The bat is a primary animal associated with fictional characters of the night, both villains, such as Dracula, and heroes, such as Batman.
Three U.S. states have an official state bat. Texas and Oklahoma are represented by the Mexican free-tailed bat; Virginia is represented by the Virginia big-eared bat.